 |
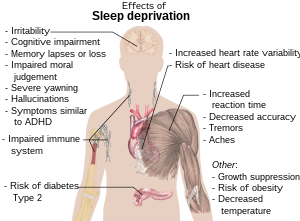
| Main health effects of sleep deprivation (See Wikipedia:Sleep deprivation). Model: Mikael Häggström. To discuss image, please see Template talk:Häggström diagrams (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
Although most people get around five to seven hours of sleep a night, experts caution that number should really be somewhere closer to eight hours of sleep. "The problem with being chronically sleep-deprived (as in, missing one to two hours nightly) is that the body perceives the sleep loss as a "stress," which increases levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol (which interferes with insulin function)," says Shawn Talbott, nutritional biochemist and author of "The Secret Vigor: How to Overcome Burnout, Restore Biochemical Balance, and Reclaim Your Natural Energy."
That means blood sugar regulation is compromised and you'll crave more sweets and junk food. The increased appetite for unhealthy snacks puts you at risk for abdominal weight gain, diabetes and obesity.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.